Entrepreneurs often need financial resources to continue their company's business model and unlock its growth and profitability potential. A startup's natural path in this process is to seek equity from a strategic or financial partner, resulting in the dilution of the investors' and founders' stakes. This type of move can represent a high opportunity cost due to the immediate dilution of shareholders.
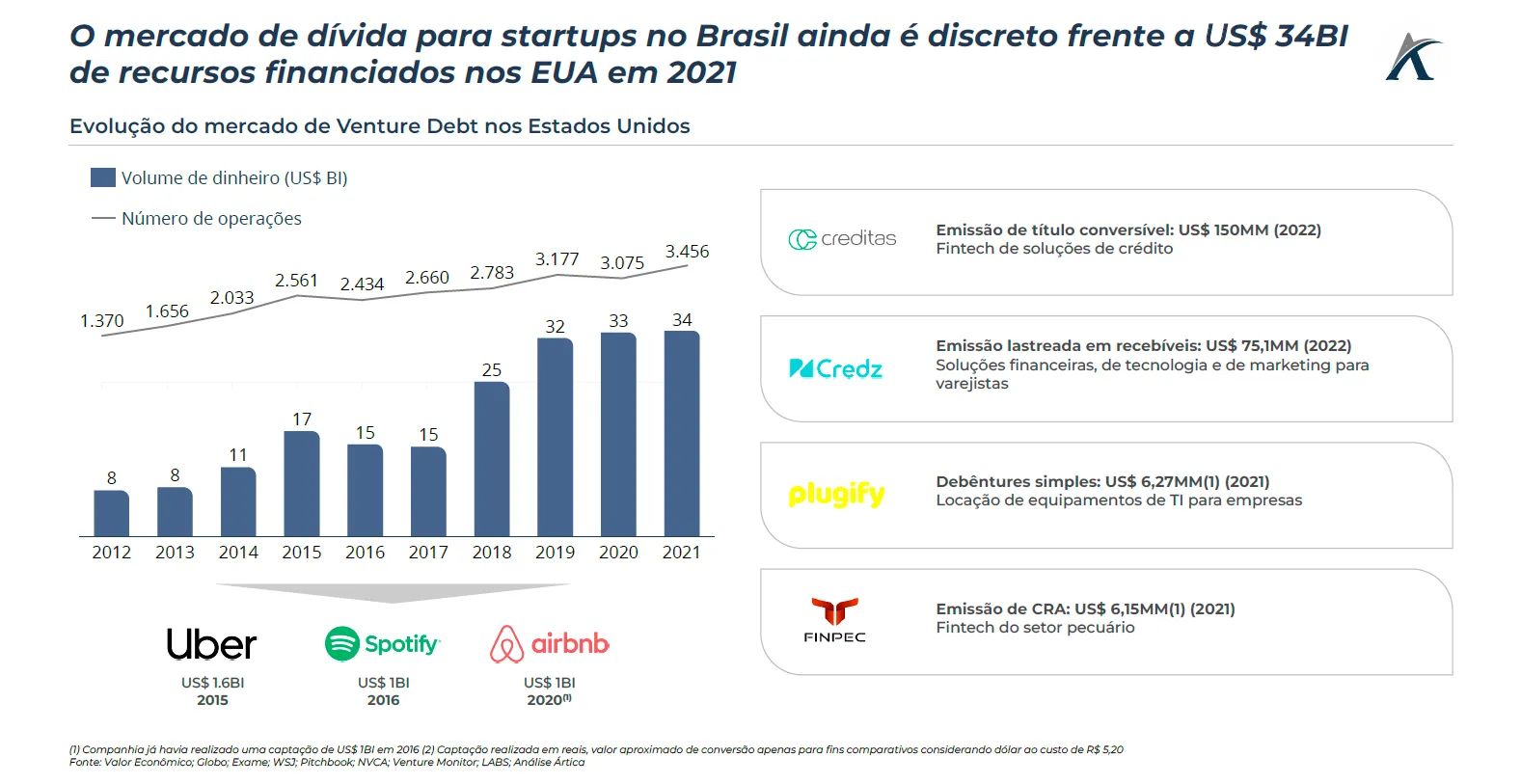
One alternative to mitigate the difficulty of initial funding for startups is to opt for Venture Debt, which uses a lender as a backer for the financial contribution. Venture Debt investments in Brazil are still modest compared to the American market. In the US, this debt market generated US$1,400,000 in 2021 through 3,000 investments.
Venture Debt is a type of financing for companies in the early stages of their business, meaning they lack collateral or sufficient cash flow to justify traditional borrowing, such as lines of credit from banks. This modality involves debt with the possibility of a premium for conversion into equity for the lender, usually a credit investment fund. In this sense, unlike a bank line focused on paying installments and interest on the debt, the Venture Debt lender is also interested in the potential gains from the company's growth.