The S&P 500, the leading barometer of the U.S. stock market, transcends borders, reflecting the structural transformations of the global economy over time. Its sectoral composition evolves in response to the emergence of new technologies, the reinvention of established sectors, and market dynamics. Analyzing these transformations is crucial for strategic decision-making in investments and mergers and acquisitions (M&A).
1990-2000: The Era of Diversification:
In this decade, the index showed greater sectoral diversification, with emphasis on energy, retail, consumer goods and industry. Giants such as Exxon Mobil and General Electric led the way, highlighting the importance of physical production and commodities in the global economy.
2000-2010: The Rise of Technology and the Financial Crisis:
Technology began to gain momentum with the popularization of the internet and the advancement of cloud computing. Microsoft and IBM rose in the rankings. The financial sector, which is highly representative, was severely impacted by the 2008 crisis, which reconfigured the banking and insurance landscape.
2010-2020: The Consolidation of the Digital Era:
Technology has consolidated its dominant position, with Apple, Amazon and Alphabet leading the index, driven by digital, e-commerce and cloud services. Traditional sectors, such as industry and energy, have lost relative relevance.
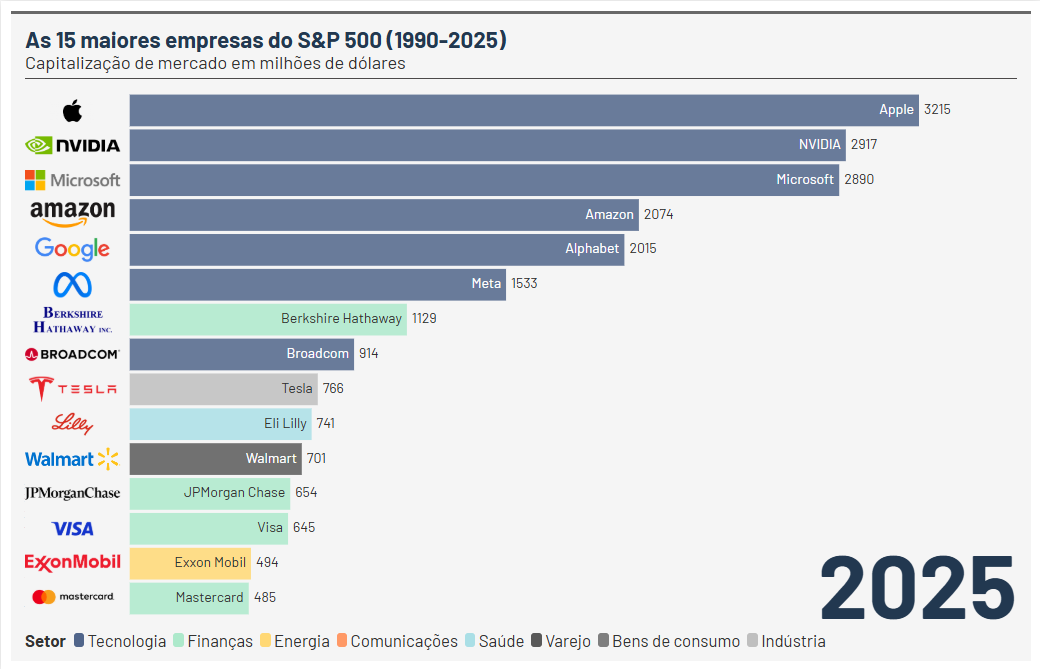
2020-2025: The Age of Artificial Intelligence:
Concentration in the tech sector has reached unprecedented levels, accelerated by the pandemic and the rise of artificial intelligence. Nvidia, driven by demand for specialized chips, has emerged as one of the biggest names in the S&P 500, symbolizing the new era of technology.
We invite you to explore the transformation of the 15 largest companies in the S&P 500 year by year, from 1990 to 2025, and to reflect on how technology is redefining the market.